Understanding Attack Surface Exposures in Ransomware Attacks
- Mohnish Singh

- Dec 22, 2024
- 2 min read
Attack Surface Exposure refers to the various vulnerabilities and entry points within an organization's digital environment that can be exploited by cybercriminals. These exposures can include internet-facing assets, internal systems, software vulnerabilities, and human factors like social engineering. The broader the attack surface, the more opportunities attackers have to infiltrate systems and deploy ransomware. Ransomware in India has emerged as a pressing concern for businesses, institutions, and individuals. Over the years, there has been a surge in ransomware attacks in India that have targeted a broad spectrum of entities, leading to substantial financial losses and reputational damage.
India is currently facing a critical cybersecurity crisis, marked by a surge in ransomware attacks that have severely disrupted essential services and instilled widespread fear among citizens. The alarming frequency and impact of these incidents underscore the urgent need for immediate and robust cybersecurity measures.
Recent attacks include:
AIIMS Delhi Attack (2023): This attack disrupted healthcare services by shutting down servers and potentially compromising patient data, emphasizing vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure.
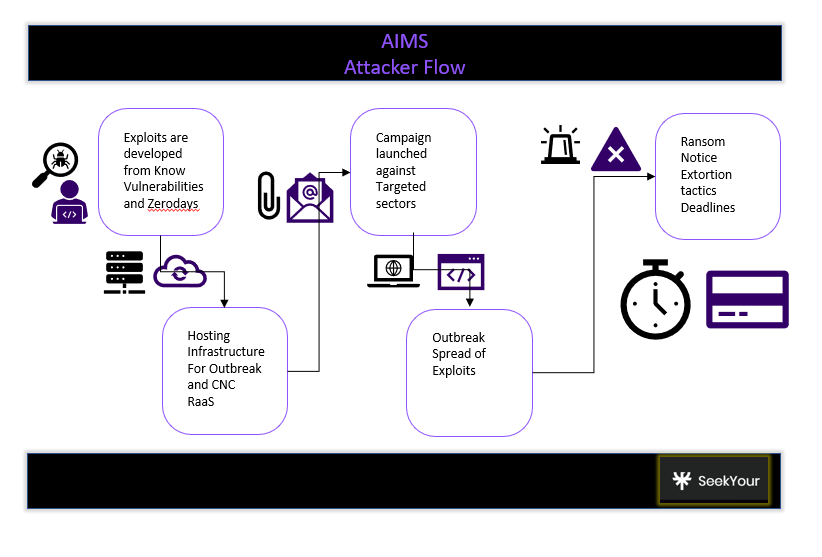
AIIMS attacker workflow Telangana and Andhra Pradesh Power Utilities Attack (2023): A ransomware attack brought down power utility systems across these states, showcasing how interconnected systems can amplify the impact of such attacks.

LockBit 3.0 Attack LockBit 3.0 Attack on Fullerton India (2024): This attack involved a ransom demand for sensitive data, highlighting the targeting of financial institutions.
SpiceJet Attack (May 2024): Ransomware slowed flight operations, affecting numerous passengers and illustrating the potential for disruption in the transportation sector.
Mirai Botnet Malware Attack: Targeting IoT devices, this attack affected millions of devices and underscored vulnerabilities in network security.
Small and medium businesses (SMBs) and enterprises are stepping up their efforts against ransomware, from assessing software suppliers to implementing cloud solutions and boosting employee education. However, the increase in organisations paying the ransom only emboldens cybercriminals, fuelling more relentless attacks.

To effectively mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks, organizations should adopt a multi-faceted approach:
Proactive Attack Surface Management (ASRM): Regularly assess and manage vulnerabilities across all digital assets to reduce exposure. Organizations with a lower Cyber Risk Index (CRI) are significantly less likely to experience attacks.
Regular Vulnerability Assessments: Conduct frequent assessments to identify and patch outdated software and misconfigured systems that could serve as entry points for attackers.
Security Awareness Training: Educate employees about common attack vectors such as phishing and social engineering to reduce human error that can lead to breaches.
Implement Strong Access Controls: Use multi-factor authentication and limit access to sensitive systems to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Backup Data Regularly: Maintain up-to-date backups of critical data to ensure recovery in case of an attack, minimizing potential losses from ransomware encryption.
Monitor Third-party Risks: Evaluate the security practices of third-party vendors to ensure they do not introduce additional vulnerabilities into your organization.


Comments